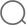
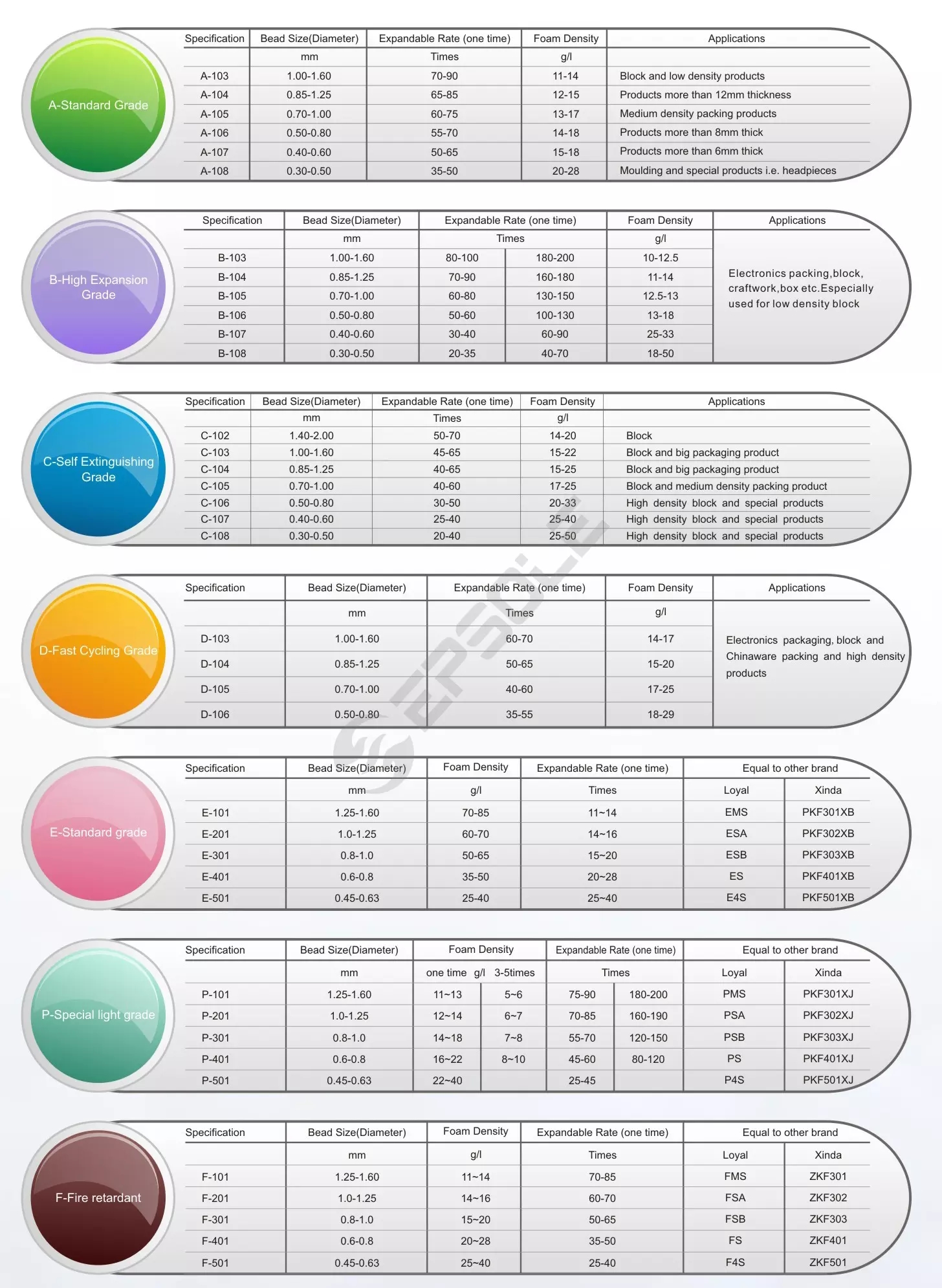
In EPS products obtained by inflating and fusing polystyrene particles, the blowing gas used to inflate the particles and obtain foam is ‘Pentane’. Pentane, an organic component, is replaced by air in a very short time during and after production, after allowing the formation of many small pores in the particles. The pentane gas released turns into CO2 and water vapor-H2O, which are already in the atmosphere. With the release of pentane, still air is trapped in the large number of small closed porous cells in the material (3-6 billion in 1 m3 EPS depending on density). 98% of the material is inert air,
After the material is supplied as raw material in small granules, it goes through pre-puffing process. Meanwhile, the pentane gas in the particles and the air are exchanged and the desired density of the material is largely achieved at this stage. Later, the expanded particles rested in a special silo are fused with each other with the help of water vapor in the mold and the material gains its properties. As a result of the fusion of the grains with each other, a continuous mass formed by polygons fused with each other without any gaps in the honeycomb appearance occurs. Subsequent production steps vary according to the usage area of the material (for thermal insulation purposes or as packaging material).

 Tel:
Tel:

 English
English